
U.S. ENERGY INFORMATION ADMINISTRATION
WASHINGTON DC 20585
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
July 9, 2024
EIA expects rising electricity demand and natural gas prices to affect electricity fuel mix for the rest of 2024
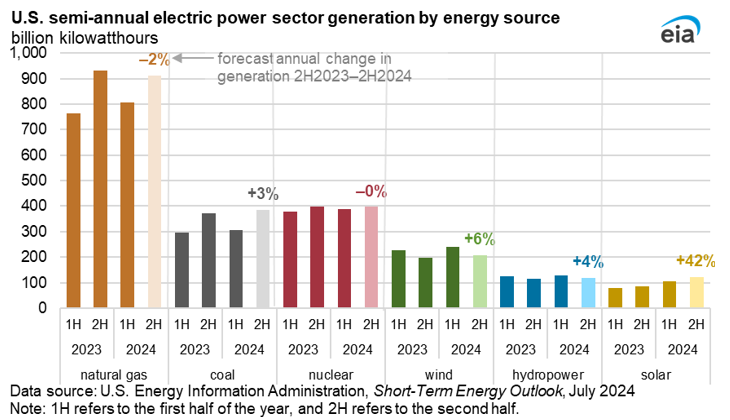
EIA expects electricity demand will be about 2% higher in the second half of 2024 than in the same period of 2023, which means renewables and coal will have to provide more power to meet demand.
"The increase in electricity demand paired with a decrease in natural gas generation creates a gap between the power we need and the power being produced," said EIA Administrator Joe DeCarolis. "Utilities will look for a more economical alternative as natural gas prices go up. Since so much renewable capacity has been coming online the last couple of years, we expect renewables—especially solar—to fill most of the gap in the power mix. We expect utilities will also look to coal as a less expensive fuel source the rest of the year."
EIA expects 42% more electricity generation from solar in the second half of the year than in the second half of 2023. EIA forecasts 6% more generation from wind, 3% more generation from hydropower, and 3% more generation from coal over the same time period.
The hotter-than-normal start to the year contributed to about 5% more U.S. electricity generation in the first half of 2024 than during the same period in 2023, as air-conditioning use increased in response to higher temperatures. EIA expects about 2% growth in electricity generation in the second half of the year as continued growth in demand in the commercial sector, which includes growing demand from data centers, is moderated somewhat by temperatures that remain relatively similar to the second half of last year.
Other highlights from the July STEO include:
 Crude oil prices. EIA expects Brent crude oil prices, the international marker for the oil market, to average $89 per barrel in the second half of 2024 and $91 in the first quarter of 2025. Those average prices are up from the average of $84 per barrel for the first half of this year. The price increase largely comes from EIA’s forecast of declining global crude oil supplies as global oil production decreases and global consumption of liquid fuels increases.
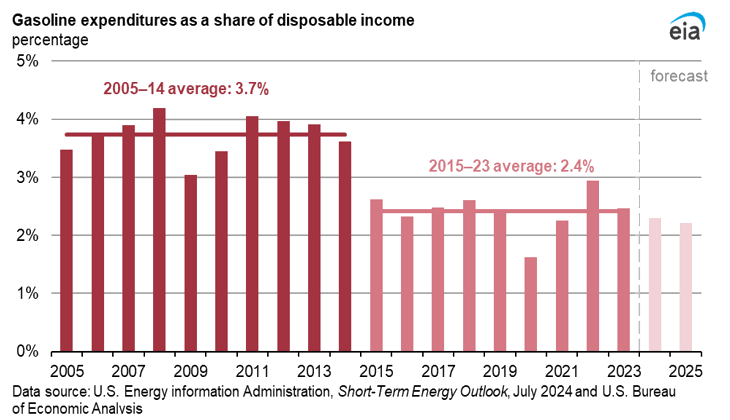
Crude oil prices. EIA expects Brent crude oil prices, the international marker for the oil market, to average $89 per barrel in the second half of 2024 and $91 in the first quarter of 2025. Those average prices are up from the average of $84 per barrel for the first half of this year. The price increase largely comes from EIA’s forecast of declining global crude oil supplies as global oil production decreases and global consumption of liquid fuels increases.- Household gasoline expenditures. EIA expects that U.S. households will spend an average of about 2.3% of their disposable income on gasoline in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025. EIA forecasts that increases in vehicle efficiency and household income will offset forecast growth in gasoline prices and consumption.
The full July 2024 STEO is available on the EIA website.
EIA Press Contact: Chris Higginbotham, EIAMedia@eia.gov
EIA Program Contact: Tim Hess, STEO@eia.gov
